티스토리 뷰
● 도입

- method를 지정하는 방법 중 마지막으로 constructor를 지정하는 방법을 알아보자
● 실습
1. User class의 constructor
package com.fastcampus.functionalprogramming.chapter5.model;
public class User {
private int id;
private String name;
public User(int id, String name) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User [id=" + id + ", " + (name != null ? "name=" + name : "") + "]";
}
}- 기존 방법으로 User class의 instance는 아래와 같은 방법으로 만든다.
public class Chapter5Section3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
User user = new User(1, "Alice");
}
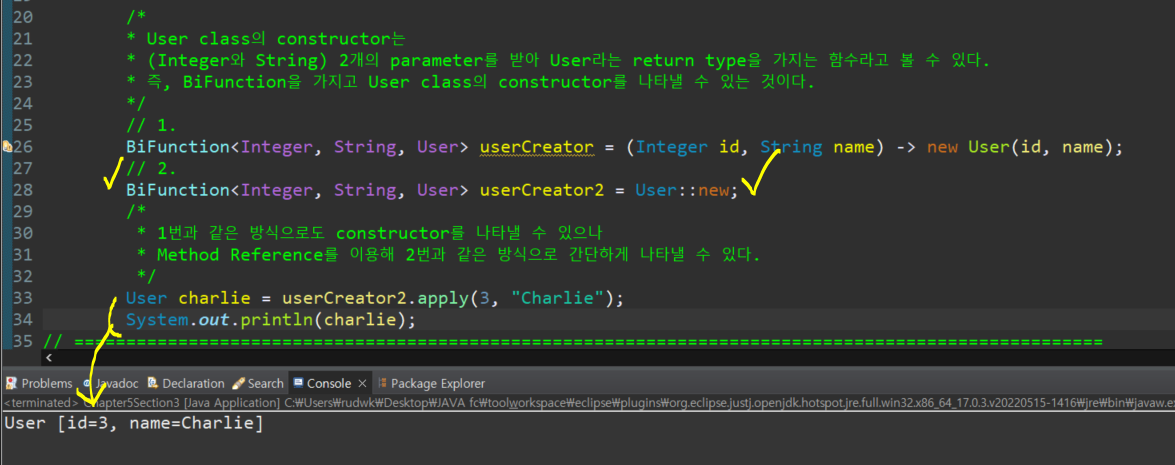
}- User class의 constructor는 (Integer와 String) 2개의 parameter를 받아 User라는 return type을 가지는 함수라고 볼 수 있다.
- 즉, BiFunction을 가지고 User class의 constructor를 나타낼 수 있는 것이다.
[BiFunction interface]
package java.util.function;
import java.util.Objects;
@FunctionalInterface
public interface BiFunction<T, U, R> {
R apply(T t, U u);
}package com.fastcampus.functionalprogramming.chapter5;
import java.util.function.BiFunction;
import com.fastcampus.functionalprogramming.chapter5.model.User;
public class Chapter5Section3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1.
BiFunction<Integer, String, User> userCreator = (Integer id, String name) -> new User(id, name);
// 2.
BiFunction<Integer, String, User> userCreator2 = User::new;
/*
* 1번과 같은 방식으로도 constructor를 나타낼 수 있으나
* Method Reference를 이용해 2번과 같은 방식으로 간단하게 나타낼 수 있다.
*/
User charlie = userCreator2.apply(3, "Charlie");
System.out.println(charlie);
}
}
2.
- car List를 만들어서 return 해보자
package com.fastcampus.functionalprogramming.chapter5.model;
public abstract class Car {
protected String name;
protected String brand;
public Car(String name, String brand) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.brand = brand;
};
public abstract void drive();
}- abstract class인 Car class를 상속 받은 3개의 class를 만들었다.(Sedan, Suv, Van)
package com.fastcampus.functionalprogramming.chapter5.model;
public class Sedan extends Car {
public Sedan(String name, String brand) {
super(name, brand);
}
@Override
public void drive() {
System.out.println("Driving a sedan " + name + "from " + brand);
}
}package com.fastcampus.functionalprogramming.chapter5.model;
public class Suv extends Car {
public Suv(String name, String brand) {
super(name, brand);
}
@Override
public void drive() {
System.out.println("Driving a Suv " + name + "from " + brand);
}
}package com.fastcampus.functionalprogramming.chapter5.model;
public class Van extends Car {
public Van(String name, String brand) {
super(name, brand);
}
@Override
public void drive() {
System.out.println("Driving a Van " + name + "from " + brand);
}
}package com.fastcampus.functionalprogramming.chapter5;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.function.BiFunction;
import com.fastcampus.functionalprogramming.chapter5.model.Car;
import com.fastcampus.functionalprogramming.chapter5.model.Sedan;
import com.fastcampus.functionalprogramming.chapter5.model.Suv;
import com.fastcampus.functionalprogramming.chapter5.model.User;
import com.fastcampus.functionalprogramming.chapter5.model.Van;
public class Chapter5Section3 {
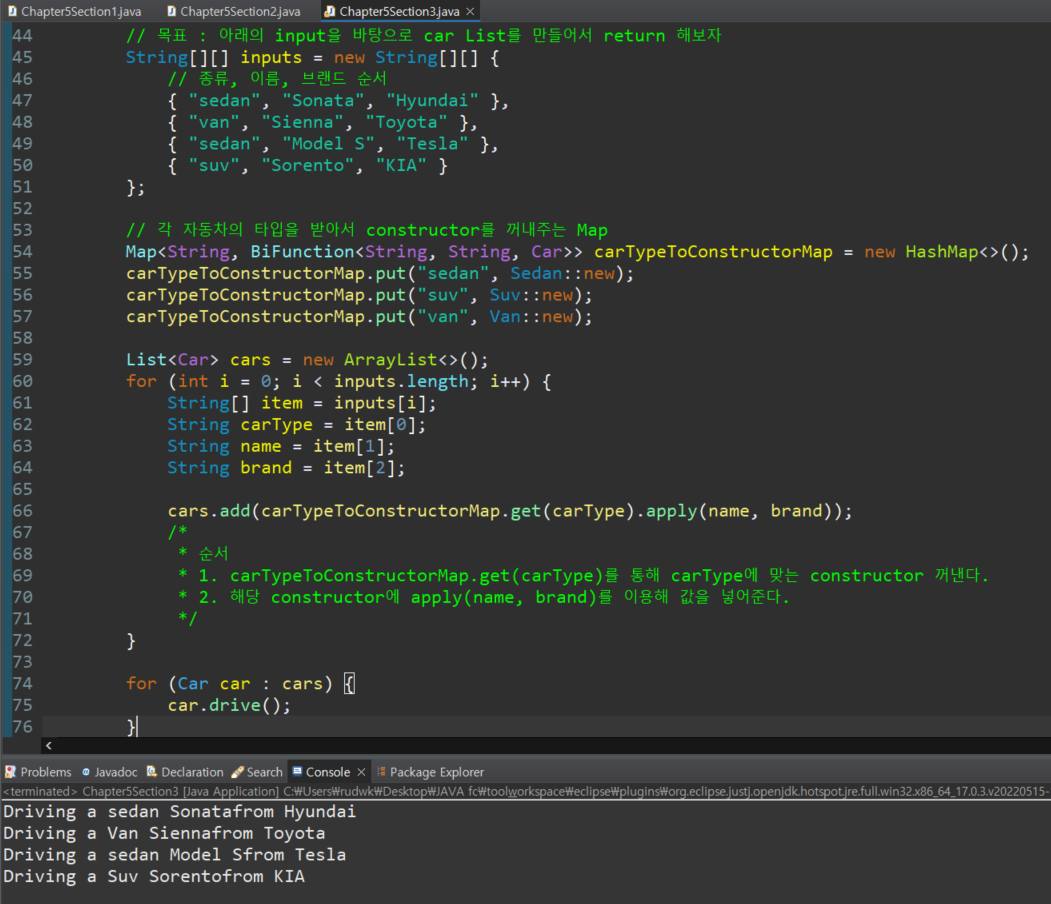
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 목표 : 아래의 input을 바탕으로 car List를 만들어서 return 해보자
String[][] inputs = new String[][] {
// 종류, 이름, 브랜드 순서
{ "sedan", "Sonata", "Hyundai" },
{ "van", "Sienna", "Toyota" },
{ "sedan", "Model S", "Tesla" },
{ "suv", "Sorento", "KIA" }
};
// 각 자동차의 타입을 받아서 constructor를 꺼내주는 Map
Map<String, BiFunction<String, String, Car>> carTypeToConstructorMap = new HashMap<>();
carTypeToConstructorMap.put("sedan", Sedan::new);
carTypeToConstructorMap.put("suv", Suv::new);
carTypeToConstructorMap.put("van", Van::new);
List<Car> cars = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < inputs.length; i++) {
String[] item = inputs[i];
String carType = item[0];
String name = item[1];
String brand = item[2];
cars.add(carTypeToConstructorMap.get(carType).apply(name, brand));
/*
* 순서
* 1. carTypeToConstructorMap.get(carType)를 통해 carType에 맞는 constructor 꺼낸다.
* 2. 해당 constructor에 apply(name, brand)를 이용해 값을 넣어준다.
*/
}
for (Car car : cars) {
car.drive();
}
}
}
'Backend > Java8' 카테고리의 다른 글
| #15 Stream이란? / Stream 만들어보기 (1) | 2022.10.04 |
|---|---|
| #14 Method Reference를 이용해 기존 예제를 더 간단하게 (0) | 2022.10.03 |
| #12 Method Reference2 (0) | 2022.09.24 |
| #11 Method Reference - 기존에 만들어놓은 Method를 지정하는 방법 (0) | 2022.09.23 |
| #10 Comparator : 비교를 위한 인터페이스 (1) | 2022.09.22 |
공지사항
최근에 올라온 글
최근에 달린 댓글
- Total
- Today
- Yesterday
링크
TAG
- MySQL
- 코딩테스트
- Phaser3
- DART
- db
- Advanced Stream
- jpa
- Spring Boot
- 빅데이터
- 메모리
- 빅데이터 분석기사
- git
- spring
- SpringBoot
- nosql
- MongoDB
- 운영체제
- Stream
- 자료구조
- 코테
- API
- 프로세스
- 알고리즘
- java
- Phaser
- Java8
- SQL
- 프로그래머스
- node.js
- OS
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
글 보관함
